Is It The Cholesterol That Makes Eggs Bad For You?
The nutritional facts on eggs have been all over the place since the 1970s when we were first told to reduce dietary cholesterol as a means to lessen our risk of heart disease.
And the egg became Public Enemy #1.
But all those reports failed to mention that our diet, what we eat, contributes to no more than 15% of our cholesterol. JUST 15%!
Can you envision the tiny egg in a jail suit behind bars screaming… “I’m innocent! I’ve been framed!”?
Cholesterol is not the enemy. You can learn more about why we need cholesterol for brain health and good mood, and why cholesterol isn’t the “Bad Guy” inside this article.
Okay, let’s get into the health and nutritional facts on eggs…
Are Eggs Fatty?
Perhaps you avoided eggs for decades? Used only the egg whites or…gag…ate products that mimic eggs?
You avoided fat.
And you were careful not to consume too much cholesterol. Right?
It’s interesting that the ‘fat and cholesterol-watching generation’ is now experiencing an epidemic of fat and cholesterol starved brain syndrome aka Alzheimer’s. Following those low fat and anti-cholesterol directives has led us down a dangerous, life altering path.
Of course, Alzheimer’s is about brain health. But, what about waistline health? Won’t all that fat from an egg just add to an already expanding middle?
Actually, no.
Fat foods are not fattening foods.
And cholesterol foods are not cholesterol rising foods.
We’ll get into those facts down below.
For now, take a look at the video below for the nutritional facts on eggs that nobody talks about…
The Nutritional Facts On Eggs That Nobody Talks About...
Are Eggs Healthy?
Egg benefits for health are many.
But to truly appreciate the egg, it’s helpful to SHIFT from viewing the egg and food in general from a surface dweller’s perspective and into a deep dive.
When it comes to food, there are so many different tribes…
- The food purists proclaim fruits, vegetables, whole grains are the answer!
- The organics don’t touch anything that isn’t clean, isn’t organic, isn’t wholesome in appearance.
- The eat pretty folks gravitate towards foods that make for great instagram uploads, FB posts, and magazine covers.
And on a surface level, all three food tribes have validity.
But when you look under the hood, the engine driving those beliefs is leaking oil… badly.
What does that mean?
It means every food, despite its nutritional profile or appearance, carries a specific impact on the body’s ability to be either in fat accumulation mode or in fat releasing mode.
Science isn’t necessarily sexy, colorful or pretty. But it does provide sanity.
Any of us in pursuit of health gain and weight loss needs to know with absolute and calm certainty how to enable our body to release fat instead of accumulate it or hold on to it.
Am I right?
Certainty. It’s so powerful.
- Are you certain if you join the latest kick-ass vibe exercise tribe you’re gonna lose the weight?
- Are you certain if you eat nutritionally dense and organic you’re going to lose the weight?
- Are you certain if you eat morally and locally and sustainably, you’re going to lose the weight?
Here’s the thing. The human body is very good at gathering body fat. Gaining weight requires little to no thought or understanding of biological processes.
But losing weight?
This is where we need to be smart. We need to understand how a body loses weight. Internal conditions must be exactly right for a body to be able to release body fat. In order to lose body fat a body must be permitted to USE its body fat.
“Excuse me, do you have permit for that?”
It’s true.
No one loses weight. They USE their weight. THAT is weight loss. Body fat must be used up. Body fat doesn’t melt or evaporate. Body fat, under the right conditions or ‘permit’, releases from storage, circulates through the bloodstream and is delivered to cells seeking fuel. THAT is how a body reduces their weight, or more correctly, reduces body fat.
Learn Why Weight Loss Exercise Fails -> Read More.
Okay. Back to our main topic, “Nutritional Facts On Eggs”.
You see for an egg, it’s not any ‘thing’ in the nutritional panel. Not the choline. Not the carotenoids (What are they anyway? We’ll hit that in a bit.) Not the ‘perfect’ protein. It’s not what any of these health-supporting components of an egg do that assists with weight loss.
First, Let’s Look At What Eggs Do
Does anyone else remember the jingle from the 80s?
Sing it with me…..“the incredible, edible egg.”
Naysayers will poo poo the humble egg’s superior protein content with the argument that our body’s need for protein is exaggerated. And they are right!
What’s Another Word For Too Much Protein? SUGAR 🙁
Oftentimes we are misled into thinking that since protein is good, then more protein is even better. However, protein comes with its unique set of pitfalls like quality, absorbability, and most importantly for weight loss, whether, and how much, our body actually needs it.
If we end up consuming more protein than we need at any given time, the extra, unused protein behaves like a carbohydrate. It converts to sugar, just like every carbohydrate we consume. And that is the pitfall. The extra protein generates more glucose / sugar in our body. And that sabotages weight loss.
When It Comes To The Best Nutritional Facts On Eggs, Protein Tops The List
That’s because one egg delivers the highest quality protein, naturally occurring in nature which is both readily absorbed by the body and in a not-too-much quantity. Actually, it’s just the right amount. There is no wondering or guesswork required. So regarding protein, an egg is a no brainer good idea for both health and weight.
Anti-egg people generally consume protein from plants. That’s cool. However, plant protein supplies the building blocks for plants while animal protein supplies building blocks for, well, animals.
Despite how some of us would like to feel about ourselves, people are animals. Our metabolic systems are designed to operate optimally on fat and protein. Fat and protein are essential.
However, carbohydrate is non-essential.
Plants are carbohydrates. So, when using plants for protein, we naturally take in an even greater amount of glucose/carbohydrate to get a small amount of protein. It’s the over-consumption of carbohydrate that takes us down.
What Else Does The “Incredible, Edible Egg” Have To Offer Us Nutritionally?
Have you come across fear mongering out there?
- Eggs are not safe!
- Eggs just might kill you!
- And even this one…. eating eggs is like smoking cigarettes! (insert eye-roll here)
This author declares just the opposite.
Eating eggs is not at all like smoking cigarettes.
Eating eggs is like taking in a daily dose of sunshine.
Unique, Little-Known Egg Benefits For Health Includes Better Mood (Sunshine on a Plate)
Very few foods contain Vitamin D. Egg yolks, the sunshine yellow-orange part, are one of nature’s richest sources of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is so essential to the body that virtually every tissue including the brain, heart, muscles, and immune system has vitamin D receptors. That tells us that Vitamin D is needed at every level for the body to function.
Some of the roles it plays include activating genes that regulate immune function and supporting insulin production. Those two functions alone support overall health and healthy weight. Immune function guards against infection and inflammation while insulin production ensures blood sugar regulation. A body cannot survive without its immune system. And a body cannot survive without insulin. Vitamin D upholds both of these.
Both of these promote good feeling and upbeat mood. Everyone feels better when the sun comes out and the temps warm up enough that we can comfortably get outdoors.
When ultra-violet rays from the sun meet the cholesterol in our skin, Vitamin D is the result. But it can be challenging to get enough of the Vitamin D stimulating rays if we live in a part of the world where outdoor time is limited and daily sunshine on our skin is just not going to happen.
An egg is arguably the easiest and please-iest way of taking in some D every day, especially if our body is challenged to produce it by itself. If no sunshine is your fate, try some sunshine on your plate.
Look At The Egg Nutrition Facts And You’ll “See” How Eggs Support The Eyes & Brain Health
Two of our body’s most critical components: eyes and brain, get a boost from eggs. Both of these are quite susceptible to age-related decline or health bankruptcy.
Eggs provide important vitamins and minerals. In addition to vitamin D which is also key for the absorption of calcium, there’s phosphorus, and vitamin A for healthy vision, skin, and cell growth, plus two B-complex vitamins that your body needs for converting food into energy.
Eggs are also a very good source of riboflavin, selenium, and are also high in carotenoids. Carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, along with Vitamins C and E, zinc and the omega-3 fatty acids play a powerful role in eye health.
They can help prevent cataracs, clouding of your eye lens. They may also fight the most-likely cause of vision loss when you’re older: age-related macular degeneration.
Interesting to note. webmd.com lists six nutrients for eye health.
All six of those eye-health nutrients are found in one egg.
One Of The Many Egg Benefits For Health… Alzheimer’s Protection
For any of us seeking to avoid Alzheimer’s or simply to maintain critical brain functioning, eggs deliver one of nature’s best sources of choline. Ensuring cell membrane fortification and brain detoxification, choline in eggs not only supports the brain’s ability to function optimally, but to ward off progression of age-related memory loss and dementia.
Good brain function, including regeneration of nerve cells, depends on saturated fat. And once again, eggs deliver.
Nutritional Facts on Eggs for Weight Loss
Egg-cellent for Weight
It’s not any “thing” in the nutritional panel. Not the choline. Not the carotenoids, Not the ‘perfect’ protein. It’s not what any of these health-supporting components of an egg do that actually assists with weight loss. It’s what eggs DON”T do that supports weight loss.
Take a look at the nutrition breakdown. Look for the goose egg. The zero. What does an egg NOT contain. You got it. Carbohydrate.
Now. Just for the record, carbohydrate is neither a good thing nor a bad thing. It’s just a thing. It’s a thing, just like fat is a thing and just like protein is a thing.
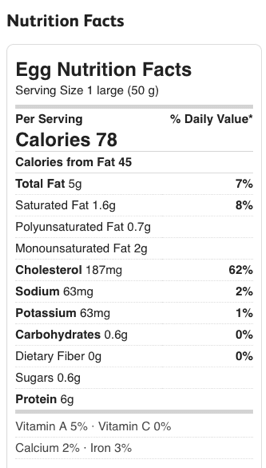
They are the three macronutrients. And each macronutrient (fat, protein, carbohydrate) impacts the body quite specifically. And it’s their specific impact on the pancreas’ secretion of insulin that is paramount. Because when it comes to weight loss, it’s the hormone insulin that is boss.
Fear mongers and surface dwellers, the water skiers of life falsely ‘see’ dietary fat as the culprit. They ‘believe’ fat makes a body fat. But it’s the hormone insulin that makes a body fat. And if we are in pursuit of weight loss, managing insulin is priority. Which begs the question, “Which foods stimulate insulin?”
And the answer is Carbohydrate. Protein can stimulate insulin a bit. Not much. Fat very little to none at all. But carbohydrate? That’s a big 100% stimulant of insulin. All carbohydrate, even the plants ie fruits, vegetables and grains, stimulate insulin. But the butter (all fat)? Nope. The eggs (fat and protein)? No.
Nutritional Facts on Eggs vs Cereal
Here are a few food comparisons. For losing or managing weight, less carbohydrate suppresses insulin which translates into less body fat. Take a look.
Nutritional Value Of Eggs vs Cereal
1 cup of a multi-grain breakfast cereal delivers about 20g carbohydrate.
An egg has 0g of carbohydrate.
Who eats just one cup of cereal? Generally it’s about 3 cups. Total 60 carbohydrate for the cereal. But if we add two more eggs? Still 0 carbohydrate.
Conclusion: Cereals stimulate insulin. Eggs don’t.

Nutritional Value Of Eggs vs Oatmeal
1/4 cup of Quaker Steel Cut Oats delivers roughly 24g carbohydrate
Egg = 0 Carbohydrate
Again, who eats 1/4 cup of oatmeal? And how many of us eat it plain? Brown sugar? Fruit? Honey? All add more and more carbohydrates. Crikey. You see where this is going.
Conclusion: Oatmeal stimulates insulin. Eggs don’t.

Nutritional Value Of Eggs vs Fruit
1 medium Banana roughly 24g carbohydrate
Egg = 0 Carbohydrate
Fruit has to be the most glorified of real, whole food eating. It rarely takes any of the blame for an expanding waistline or debilitating pain or fueling cancer. We’ve been duped into believing that the nutritional qualities will cancel out any carbohydrate/glucose flood it generates.
And that’s just NOT true.
Conclusion: Fruit stimulates insulin. Eggs don’t.
Nutritional Value Of Egg vs Smoothie
1 pint Jamba Juice Protein Berry Workout Smoothie 56 carbohydrate
Egg = 0 Carbohydrate
The only Jamba Juice this author does is a dance move by the same name.
No carbohydrate on the dance floor, thank you.
Conclusion: Protein Smoothies stimulate insulin. Eggs don’t.

Fear Based Nutritional Facts On Eggs
Messages come through our ears and settle into the space between them. They creep into our psyche.
Take a look.
Here is a ‘reputable’ health program which not only shuns eggs but outright compares them to cigarettes, as was mentioned earlier, because of their supposed impact on arterial health. They blame cholesterol.
“The yolk is a storehouse of cholesterol, saturated fat, vitamins and minerals. One egg yolk contains 55 calories, 4.5 grams of total fat, 1.6, grams of saturated fat, 184 milligrams of cholesterol, and small amounts of vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin B6, Iron and vitamin B12.”
You see the wording. “storehouse of cholesterol and saturated fat….” How much saturated fat is in an egg? 1 gram And cholesterol? That’s 187 milligrams. You got that, right? Not grams. Milligrams.
And it goes on…
“The egg white is mainly a storehouse of protein. One egg white contains 17 calories, 0 grams of total fat, 0 grams of saturated fat, 0 milligrams of cholesterol, 0 grams of carbohydrate, and about 4 grams of protein. In addition, the egg white contains no appreciable vitamins or minerals.”
The health program that cited the above nutritional information warns about the dangers of too much protein. How much protein is in an egg? 4 grams. Is that a lot of protein? Hmmmm. No.
Cholesterol then! That’s the big scare!! The big worry! The big crock of distraction.
The warning is that eating eggs raises cholesterol putting us at high mortality risk by opening us up to conditions like heart disease and arterial plague, diabetes, and cancer.
The problem is the evidence used to support these claims are outdated, based on speculation and link eggs to an early death by a string of casual association. Any one up on the science or better yet, doing some homework and applying the science to their own lives, knows the truth.
Personally, I celebrate my cholesterol.
Back in my low fat, low dietary cholesterol life, I registered off the charts, high cholesterol. And eggs where no where to be found in my diet.
But today, a living low carbohydrate, adequate delicious fat life, my cholesterol settled right down into an optimal healthy level.
So, don’t blame the cholesterol for what the carbohydrate did.
Eggs & Cholesterol
Here’s the deal.
#1.) The cholesterol in our blood is 80% our own making. Our own making! Diet does not have a direct effect on blood cholesterol but plays a mild downstream role. Our body produces cholesterol as our body demands.
#2.) Cholesterol naturally rises in response to inflammation and stress. Carbohydrate aka glucose stresses and inflames. The more stressed and inflamed we are the more cholesterol our body produces.
#3.) Cholesterol is a responder and supporter of our well-being. Our body would not survive without it! In fact, we would die very quickly without it.
#4.) Cholesterol is a major defensive player when our body is under attack. That’s because cholesterol is a fundamental building block for so many of our body’s functioning and fortifying players. Cell Membranes. Hormones. Memory Formation.(Dementia, Alzheimer’s) Neurological Function. (MS, Parkinson’s)
So here’s the win.
When we eat foods that support weight loss by suppressing insulin, we use up body fat and reduce inflammation. As a result, cholesterol naturally lowers because our body produces less cholesterol in response to the lowering of our stress and inflammation.
Nutritional Facts On Eggs & Disease Prevention
Eggs and Heart Disease!
Heart disease is what? Heart disease is the condition when vessels, through which oxygen-rich blood flow to the heart or brain, become harder to pass through due to a hardening or thickening. Less blood makes it to the heart or brain resulting in a heart attack or stroke.
This hardening of blood vessels was once blamed on cholesterol. But cholesterol was just patching up the lining damage caused by glucose (carbohydrate). And when there is glucose there is insulin.
Insulin, NOT CHOLESTEROL is the underlying cause of thickening arteries, atherosclerosis. Insulin, being an anabolic hormone, ensures growth. Insulin promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation in the lining of vessels. Carbohydrate stimulates insulin. Fat doesn’t.
Eggs and Cancer!
Can eggs cause cancer? Actually, the cancer-scare folk warn that because eggs are protein-rich (an egg only has 4-6 grams of protein) the ‘high’ protein stimulates another hormone called IGF-1. That is the Insulin Growth Factor hormone.
IGF-1 is stimulated by growth enhancing habits such as intense, vigorous activity, resistance training, and protein consumption. The fear connect-the-dots linking the protein in eggs to an uptick in IGF-1 which could promote cancer cell growth. It’s a leap.
You see, cancer cells can utilize protein for fuel just like our healthy cells because protein converts to glucose. And glucose stimulates insulin and insulin increases the bioactivity of IGF-1. But the straightforward science is still clear.
A.) An egg delivers no more than 6 grams of protein.
B.) Eggs do not stimulate insulin.
C.) Therefore, Eggs do not stimulate an increase in IGF-1 activity.
Eggs and Diabetes!
This excerpt from a company selling a diabetes health program is an example of the use of FEAR tactics, half-truths and misinformation on eggs to further their company sales agenda:
Adults with diabetes (type 1 or type 2) are 2 to 4 times more likely to develop heart disease or stroke than nondiabetic adults. The reason for this is simple: elevated blood glucose increases the risk for all forms of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, stroke, angina, and coronary artery disease (2-4).
The second sentence states: “The elevated blood glucose is the reason a diabetic is at heightened risk for all forms of cardiovascular disease.”
Then the experts chide diabetics to not eat eggs.
But eggs don’t elevate blood glucose. This company tries to scare diabetics from eating the very foods that don’t raise blood glucose. Is there anything crazier?
Let’s be grateful for eggs!
Economical.
Accessible.
Easy to prepare.
Versatile.
Excellent nutrients.
Insulin Suppressing .
Here are a few simple tips regarding eggs.
Nutritional Facts On Eggs – Tips
1.) Buy Pastured, Organic Eggs Whenever Possible.
“Pastured” means hens have been allowed to roam freely and feed on greens, grubs, and insects which are part of their natural diet. Pasturing ensures a higher quality egg with more omega-3 fat. Some stores advertise eggs high in omega-3. These eggs came from hens fed flaxseed to boost the omega-3 level. Great choice.
2.) Buy Freshest Available, Brown or White Eggs.
Shell color has no bearing on egg quality. Always try for the freshest available. If you live in an area where local farm eggs are an option, give them a try!
3.) How Should I Cook My Eggs?
Cook on low heat to protect the fatty acids and nutrients.
Cook in butter, coconut oil, or ghee. Try adding cream cheese for a truly fluffy, delightful, and oh so satisfying egg meal.
4.) Treat Yourself To Our Featured Recipe – Eggs Saratoga! (Download the recipe here.)
Nutritional Facts On Eggs Conclusion
Eating eggs allows our body to be in body fat-releasing mode because its near-zero carbohydrate value suppresses the secretion of insulin. When insulin level remains low, body fat burning is a ‘GO’.
Fruit, oatmeal, cereals, ancient grain breads and low fat organic zucchini muffins put a body in fat accumulation mode due to the insulin stimulating high carbohydrate value.
Humans complicate things. But when we know better we do better. And when we do better we are better….even egg-cellent!
Frequently Asked Questions – Nutritional Facts on Eggs & Weight Loss
1. Can eggs help with weight loss?
Eggs can really help with weight loss because eating eggs does not stimulate our fat storage hormone.
When insulin remains low (fat based foods like eggs keep insulin low) our body fat is accessible for burning. When insulin is raised (carbohydrate-based food is blood sugar food which raises insulin) body fat burning is halted.
Because eggs are quite balanced with protein and fat and merely trace carbohydrate they are filling, satisfying, nutrient dense and keep us not hungry for hours. That is their weight loss benefit. Filling fat. Minimal to no insulin response. Appetite suppressing.
2. How should I prepare eggs for weight loss?
Preparing your eggs should align with your desired outcome.
a.) Do you want a hearty breakfast that will carry you through to lunchtime or beyond? Then try scrambled eggs with cream cheese and grass-fed butter.
b.) Do you want a non-insulin stimulating snack to carry you through the afternoon, a workout, and get you to dinner? Go for a hard boiled egg.
c.) Do you want a satisfying dinner that’ll keep you from the 8PM ghrelin-treat-seeking cravings? Try a frittata with some crumbled bacon or sausage and low carbohydrate green vegetables like broccoli and spinach.
3. How many eggs should I eat for weight loss?
Eggs do not stimulate insulin. Eat as many as you need to satisfy hunger. Eat as many as you need to keep you sated for hours. It’s the extended time between feedings (that can be created by eating eggs) when weight loss happens.
4. What are the best eggs?
Pastured eggs are best. Hens are free to roam and eat a diet that nature intended. This translates into higher nutrient content with top quality fat. Shell color doesn’t influence nutritional quality.
5. What makes eggs healthy?
Eggs are good for us for 4 important reasons.
a.) Eggs provide nutrients essential to eye and brain health, immune function, and energy conversion.
b.) Eggs provide high quality, readily absorbable protein in an ideal amount.
c.) Eggs provide critical, life-sustaining saturated fats in a perfect quantity for humans.
d.) Eggs meet our nutrient requirements of fat and protein and suppress secretion of our fat storage hormone, insulin.
6. Why are eggs good for diabetics?
Eggs are good for diabetics because they are an essential nutrient food (natural fat and protein) and not a carbohydrate (blood sugar) food. Eggs do not raise blood sugar because eggs are not carbohydrate.
This Post’s FREE Resource

About Barbara McDermott
Regarded as America's #1 Insulin Suppression Coach, Barbara is the co-founder of SHIFT Health & Wellness Solution, and the best-selling author of the groundbreaking book, ‘FOOD B.S.’, With SHIFT, Barbara brings common sense to nutrition, weight loss and health gain. Her refreshing, no nonsense approach to uncovering the truth using non-negotiable rules of science demystifies food and how to defeat chronic disease once and for all.






Love you and all your work bringing us such great information.
Thank you Susan!
And right back at you ❤️
Barb & Charlie